Introduction
Aids and Hiv are two different medical conditions, although it is difficult to tell the difference between them. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus infection caused by the HV-1 or HV-2 virus. When the virus invades the body, the white blood cells (lymphocytes) are slowly attacked. These cells form part of the body’s immune system. Once these are destroyed, the body is susceptible or open to other viruses that cause infections. These infections lead to complications that may cause death.
On the other hand, acquired immunodeficiency disease syndrome or AIDS is the most severe form of the virus when an infected person develops complications, with a complete breakdown of the immune system. It is measured by the lymphocyte count and the low levels of CD4.
History
AIDS HIV was first discovered in 1959 when the blood sample of an African man from Congo who died mysteriously was confirmed to contain the HIV virus. The outcome of the study proved that the roots of AIDS HIV came from an African ancestor. In 1982, the CDC in the US suggested that the virus is linked to the blood. A year after (1983), French scientists at the Insitut Louis Pasteur discovered the HIV virus. In 1985, the US approved the first HIV antibody blood test. Meanwhile, the World Health Organization reports that there are 33 million people suffering from AIDS HIV as of 2008. Deaths from AIDS HIV related causes reached more than 33 million in 2008.
Features

Causes of transmission
AIDS HIV is transmitted by contact with the body fluids and secretions that contain the virus. The methods of transmission involve the exchange of body fluids such blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk. Thus a lactacting mother can actually pass the HIV virus on to the baby. The saliva, urine , tears have also traces of the HIV virus but transmission from these fluids and secretions is extremely rare.
The act of transmitting the virus itself is through sexual intercourse, sharing needles among drug users, contaminated blood transfusions, and breastfeeding a child. The mother is also likely to share the virus or pass it to the child before and after birth.
Symptoms
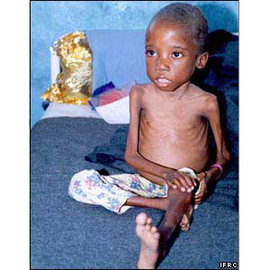
Most people who have the AIDS HIV virus exhibit no symptom at the onset of the infection. However, as the invasion progresses, there will be signs such as fever, fatigue, rashes, and swollen lymph node. These symptoms disappear after a few weeks but the swelling remains. In fact, a person who is HIV positive can live for up to a year without getting AIDS. When it gets to the AIDS stage, there are also accompanying symptoms such as rashes, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, recurring diarrhea . Infected persons develop complications such as Kaposi’s sarcoma, a painless cancer that appears as patches on the skin. It is common among homosexual men. Cancers of the lymphoma or the immune system appear inducing memory loss, personality changes as well as cancers of the cervix for women and rectum cancer for men. Death is caused by all factors such as further infections and cancers.
Diagnosis
Blood tests are used to diagnose an HIV person infected with the virus. There are several techniques to do this; blood test to detect antibodies to HIV and the viral tests or P24 antigen.
Treatment
Antiretiroviral drugs are used to treat HIV patients and there are 3 classes of drugs used to treat a patient such as nucleoside reverse transcription inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and protease inhibitors. When these treatments are done, a patient can expect to live longer unless the HIV progresses to AIDS.
Tips and comments
Protecting yourselves during sexual intercourse is still the best way of preventing the transmission of the AIDS HIV virus. It would even be better to abstain from sex to prevent transmission.
Do not share needles and syringes.
For healthcare workers, wearing rubber gloves reduces exposures to fluids and secretions of an infected person.
Comments
Most Recent Articles
-
How Hiv Causes Aids
A lot of people confuse HIV and AIDS as one and the same disease or infection. The confusion is justified as understanding medical terms is not an easy task. There are many nuances on the su...